Reliable HVAC Services for Every Season
PROFESSIONAL RESIDENTIAL & COMMERCIAL HVAC SERVICES FOR NORTHERN NEW JERSEY
At Universal Mechanical Group, we take pride in providing professional HVAC services to residential and commercial customers throughout Northern New Jersey. As a family-owned and operated business based in Clifton, we understand the importance of keeping your heating and cooling systems running at their best. That's why we offer a full range of services, including installation, repairs, and preventative maintenance, to keep your systems in top condition.
HEATING

COOLING

RESIDENTIAL

COMMERCIAL
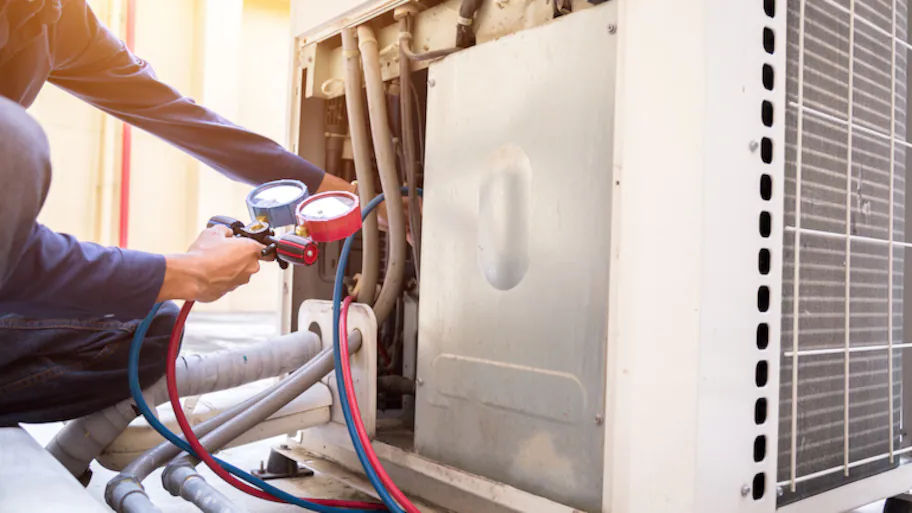


WE ARE Skilled Professionals
Our team of licensed and insured professionals is experienced in working with all types of HVAC systems, from central air conditioning to commercial boilers. We use the latest tools and techniques to ensure every job is completed to the highest standard.
In addition to our regular services, we also offer 24-hour emergency services for those unexpected heating and cooling emergencies. We understand that HVAC issues can arise anytime, and we're here to help when you need us most.


Facebook
Instagram